What is an Electric-driven Hydraulic Power Pack, and How Does it Work?
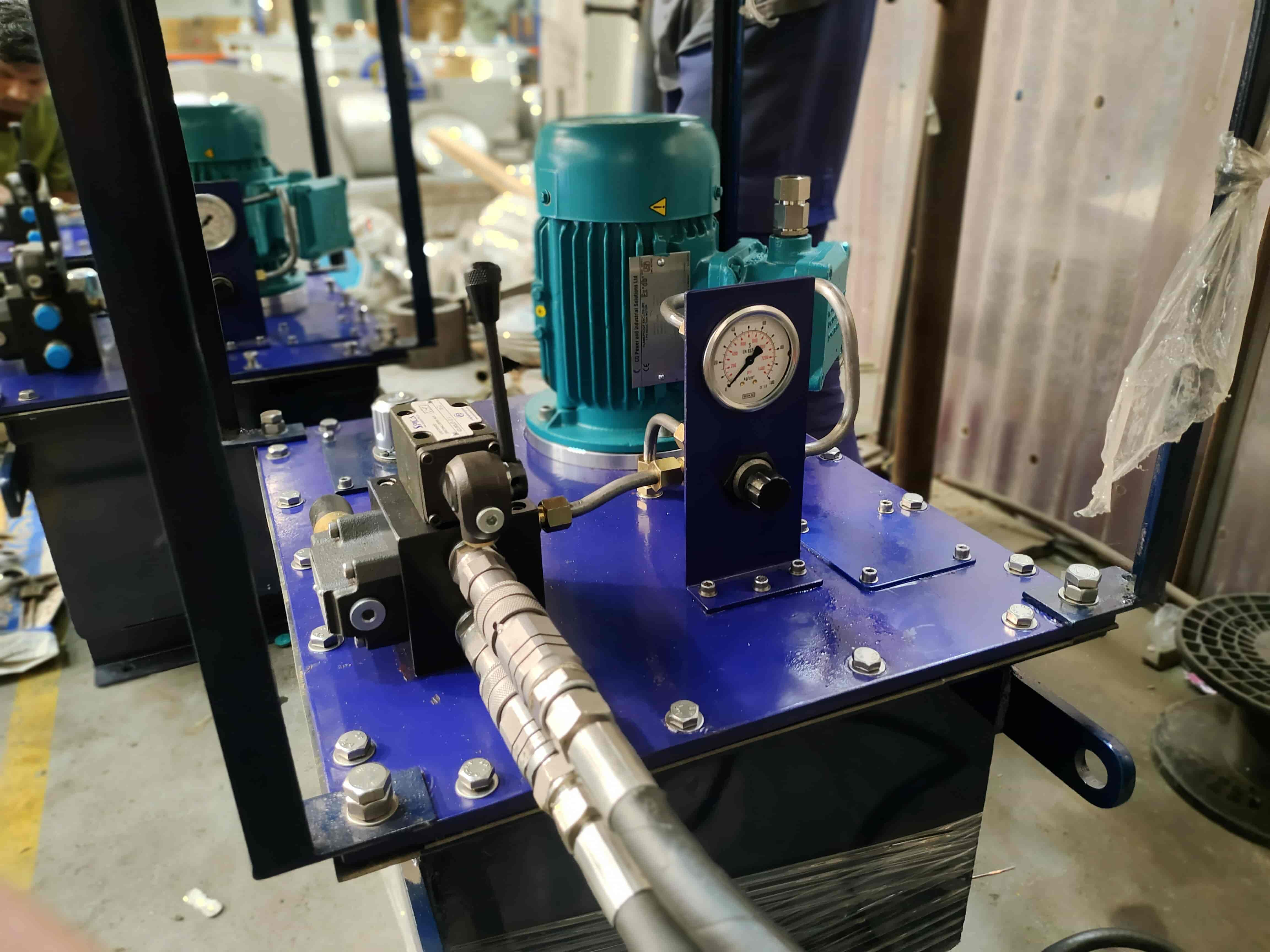

An electric-driven hydraulic power pack is used in a wide range of industrial applications. Its common uses are – oil spill response, oily water treatment, salvage pumps, ballast pumps, firefighting pumps, injection molding, construction, mining, automotive, material handling, etc.
What is the Function of an Electric Driven Hydraulic Power Pack?
The electric-driven hydraulic power pack delivers oil under pressure to hydraulic motors or cylinders. The main function of the power pack is to generate and control hydraulic power required to perform work such as lifting, pressing, or moving components.
How Does an Electric Driven Hydraulic Power Pack Work?
An electric-driven hydraulic power pack is a self-contained unit mainly comprising:
- • Electric Motor: An electric motor is the power source of the hydraulic power pack. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- • Hydraulic Pump: The hydraulic pump is responsible for generating hydraulic fluid flow. The pump converts mechanical energy from the motor into hydraulic energy.
- • Hydraulic Fluid Reservoir: The reservoir is a tank that stores hydraulic fluid. The reservoir ensures fluid temperature and viscosity is maintained at appropriate levels.
- • Control Valves: Hydraulic power is supplied to another machine via a control valve such as pressure valves, flow control valve, etc. The valves direct and regulate the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid.
- • Filter: The filter ensures contaminant-free hydraulic fluid.
- • Cooling System: The cooling system prevents the overheating of hydraulic fluid by dissipating excess heat generated during operation.
- • Accumulators: Stores hydraulic energy
- • Pressure Gauge and Sensors: Monitors the pressure and flow and also, provides feedback to the operators and control systems.
What are the Applications of an Electric Driven Hydraulic Power Pack?
Electric-driven hydraulic power packs are efficient and reliable. They are widely used in various industrial applications, a few of them are:
• Oil Spill Cleanup: Oil skimmers
• Industrial Machinery: Powering presses, injection molding machines, and conveyor systems.
• Mobile Equipment: Used in construction machinery, agricultural equipment, and material handling devices.
• Marine and Offshore: Operating winches, cranes, and other deck equipment.
• Automotive: Used in automotive lifts and other repair and maintenance equipment.
Advantages
The electric-driven hydraulic power pack finds application across industries for the advantages it offers. Some of the key advantages are:
- • Multiple pumps can be powered using one power pack
- • The power pack is skid-mounted and can be transported to remote locations
- • The single skid power pack is easy to install and operate.
- • Electric motors can offer high efficiency and precision in controlling hydraulic functions.
- • Using electricity reduces the dependence on fossil fuels, making it more environmentally friendly.
We can conclude that an electric-driven hydraulic power pack is a versatile and essential component in modern industrial and mobile hydraulic systems, providing robust power and precise control for a wide range of applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 What Are the Advantages of Using Diesel Engine Driven Hydraulic Power Packs?
A. Diesel engine driven hydraulic power packs offer high reliability and efficiency, making them ideal for demanding applications in remote or off-grid locations where electric power is unavailable. Their robust construction and fuel independence provide consistent performance and long operational life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Q.2 What applications are pump skid rotary lobe driven systems suitable for?
A. Pump skid rotary lobe driven systems are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and oil and gas, where precise fluid handling is crucial.