Reduce Water Pollution & Hazardous Waste: The Role of Automated Oil Recovery

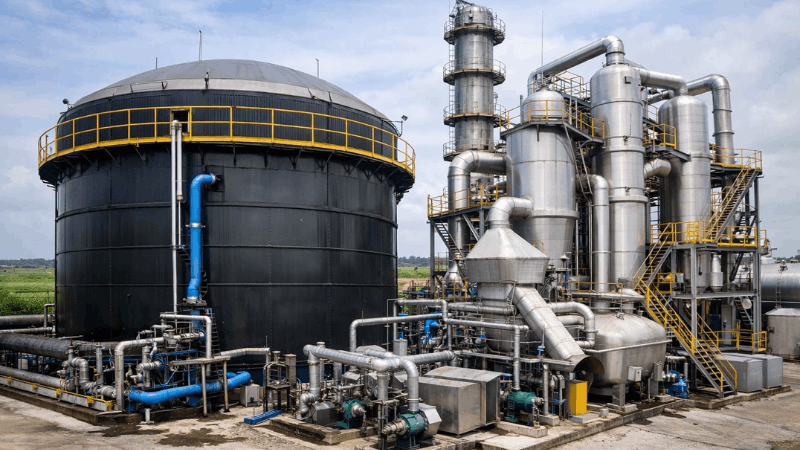
Meeting environmental regulations for oil recovery and separation demands efficiency, precision, and strict compliance with discharge limits. An Automated Oil Recovery System simplifies this process by leveraging advanced separation technologies, real-time monitoring, and minimal human intervention to recover oil from water and industrial wastewater. By integrating automation, industries can reduce waste, lower operational risks, and maintain sustainable practices while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Key Features of an Automated Oil Recovery System
- 1. Oil-Water Separation Technology – Commonly uses skimmers, centrifuges, or membrane filtration systems to efficiently separate oil from water.
- 2. Real-Time Monitoring & Control – Sensors detect oil levels and adjust recovery rates automatically to maximize efficiency.
- 3. Pumping & Storage Mechanisms – Transfers recovered oil to storage tanks for reuse or proper disposal.
- 4. Self-Cleaning & Maintenance Alerts – Minimizes downtime and ensures consistent operation.
- 5. Integration with SCADA/IoT – Enables remote monitoring and automation, improving efficiency and operational control.
Applications of Automated Oil Recovery Systems
- • Oil Spill Cleanup – Rapidly recovers oil from water bodies, minimizing environmental damage.
- • Industrial Wastewater Treatment – Removes oil before discharge, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- • Machinery & Equipment Maintenance – Recovers lubricating oil from cooling and processing systems.
While an Automated Oil Recovery System offers multiple benefits, this article focuses on reducing water contamination and minimizing hazardous waste disposal—two critical aspects of regulatory compliance.
Reduced Water Contamination
These systems play a vital role in preventing pollutants from entering natural water bodies by:
- 1. Rapid Oil Separation: Ensures removal of oil before it disperses into the water and prevents oil from mixing with water, reducing contamination levels.
- 2. Real-Time Monitoring & Automatic Adjustments: Sensors detect oil concentration and adjust separation processes for maximum efficiency. Ensures compliance with regulatory discharge limits.
- 3. Efficient Wastewater Treatment: Removes oil from industrial wastewater, stormwater runoff, and process water, ensuring clean discharge. Prevents oily effluents from contaminating rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- 4. Prevention of Secondary Pollution: Minimizes manual handling, reducing spill risks and human errors. Captures and stores recovered oil safely for recycling or environmentally responsible disposal.
- 5. Compliance with Environmental Standards: Helps industries meet PCB, MARPOL Annex I, the Clean Water Act, the Industrial Emissions Directive and other applicable discharge norms. Reduces legal risks and fines by maintaining environmentally safe operations.
Hazardous Waste Disposal
Automating oil recovery enhances oil-water separation efficiency, reduces waste generation, and maximizes oil reuse.
- 1. Improved Separation Efficiency: Automated controls and sensors optimize separation, ensuring more oil is recovered and less sludge is left as waste.
- 2. Reduced Contaminated Wastewater: Precise automation of separation and filtration processes lowers the volume of hazardous wastewater requiring treatment or disposal.
- 3. Enhanced Recycling & Reuse: Extracts high-purity recovered oil, making it suitable for reuse in industrial applications, reducing disposal needs.
- 4. Lower Human Error & Spill Risks: Automated monitoring prevents operational errors that could increase waste generation or cause spills requiring costly cleanup.
- 5. Optimized Chemical Usage: Reduces reliance on separation chemicals, lowering chemical-laden sludge classified as hazardous waste.
Ensuring Compliance and Sustainability
Automated oil recovery systems significantly reduce environmental impact, improve oil recovery efficiency, and help industries comply with key regulations, including:
- • Pollution Control Board (PCB) guidelines
- • Oil Industry Safety Directorate (OISD) standards
- • MARPOL Annex I
- • Industrial Emissions Directives, etc.
By integrating automation, industries can achieve cleaner operations, regulatory compliance, and long-term cost savings in hazardous waste management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1 How often should maintenance be performed on an oil water separator machine?
A. Maintenance for an oil water separator machine should be performed monthly, with inspections for sludge buildup, filter replacements, and pump efficiency to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Q.2 What advancements have been made in technology for oil spill cleanup equipment?
A. Advancements in oil spill equipment include automated skimmers, high-efficiency dispersant systems, drone surveillance, and biodegradable sorbents, enhancing response speed, effectiveness, and environmental safety.