Slotted Pipes And Its Application Areas
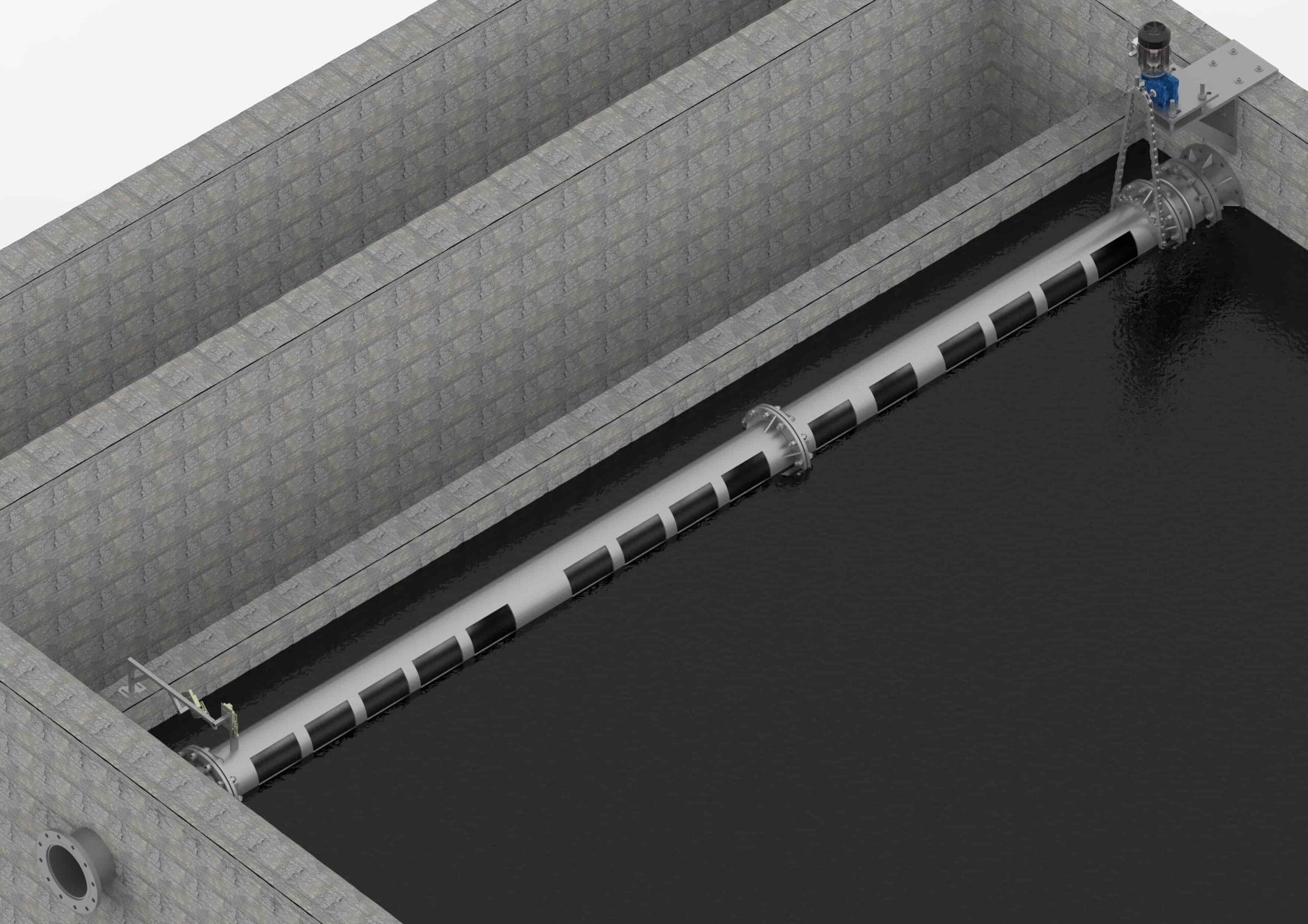
The slotted pipe is a rotary tube with horizontal ‘C’ shaped openings. The tube/pipe is mounted on the top of the tank to collect floating oil, scum, debris, etc. in industrial applications.
The slotted pipe consists of a 60° slot with reinforced gaps. The pipe can be rotated on demand either manually or by motorized arrangement. The pipe is supported on one side to a closed flange and on the other side to an open flange. The scum, oil, debris collected in the pipe gets discharged from the open flange end.
An operator removes oil, scum, debris, etc by turning the horizontal opening downward until it meets the floating oils, scum layer. The floating oil, scum, and debris then flow through the horizontal opening into the pipe to the open flange end to the collection tank. The turning of the pipe can be manual or motorized.
Slotted pipes find applications across various industries, such as oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, and groundwater exploration. Each one has unique requirements that a slotted pipe fulfils, hence it is important to understand slotted pipe for different applications.
• Oil & Gas Well: In the oil/gas wells the function of a slotted pipe is to control sand. The pipe acts as a filtrate to separate sand in the oil/gas wells. Different grades and types of slotted pipes are used for different strata during oil and gas exploration.
• Slotted pipes are ideal in oil and gas wells where screens cannot be installed. They are excellent sand control choices for thermal heavy oil and bitumen reservoirs. Suitable for high CO2/H2S, SAGD, CSS, and CBM and sand control for low fines and clay reservoirs.
• Water & Wastewater Treatment: Slotted pipes handle large volumes of floating scum consisting of oil, lubricants, fats, coolants, etc. They are ideal where oil is scattered and oil removal mechanism requires a large contact area. Slotted pipes efficiently skim low to medium-viscosity oil, including scum.
• Power Plants: Power generating plants use petroleum-based products ranging from fuel oil and hydraulic fluids to lubricating greases and oils, whether coal-fired, gas-fired, hydropower, or nuclear. These lubricants support all moving parts of the power plant, resulting in some oil leaks finding its way into the process, cooling, or cleaning water that flows throughout the plant. Slotted pipes are used for conditioning recirculating water and as part of wastewater treatment before discharge into the drainage system.
• Drainage Systems: Slotted pipes are used in drainage systems to remove water on streets, highways, and parking lots. They also find application in draining excess water in swimming pools.
Slotted pipes are gaining popularity in drainage systems. The features and advantages they offer are:
• Aesthetically pleasing and inexpensive
• Durable and easy to install
• Maximum flirtation and minimum clogging
Slotted pipes require low maintenance and are effective in removing floating oils, scum, and debris. Their use in industrial, public, and urban areas differs based on the applications they serve. To understand the type, material of construction, and specifications required for your application, consult an expert to make the right choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 What are the main components of a mechanical bar screen?
A. The main components of a mechanical bar screen typically include a frame, bar racks, and a cleaning mechanism. These components work together to effectively remove debris and solids from wastewater, ensuring efficient operation of the screening process.
Q.2 How does a weir gate function in controlling water flow?
A. A weir gate functions by regulating water flow through a dam or canal. It controls the water level by raising or lowering a barrier, allowing for precise management of water flow rates and levels to meet operational needs.